Maintaining equipment and machineries as per schedules is crucial, says Pradeep Kulshrestha.
Based on practical experience on the shop floor, one would like to elaborate on the proper working of machines, as also crucial elements that need to be kept in mind by a foreman or mechanic (responsible for the task). In properly maintaining equipment or machineries by following a methodical schedule, plants can consistently deliver better outputs. After all, the performance of a machine does not deteriorate in the long term if requisite maintenance is carried out properly.
Some of the basic requirements for carrying out proper maintenance include:
Availability of machine manuals;
Availability of spare parts catalogues;
Storage of spares / lubricants / tools;
Maintenance plans;
Maintenance schedules / checklists;
Maintenance teams;
Availability of tools / spanners, etc.
The importance of maintenance
With business itself becoming global, a typical customer's basic requirements invariably are quality and timely delivery. And, changes in the very concepts on attaining world-class quality have been rendered possible by the theories and techniques advocated by modern-day experts.
So, it is important that one must use only the appropriate tools (spanners, keysets, gauges, torque spanners, etc) to avoid the improper fitting of nuts and bolts in a machine or equipment. During machine maintenance, one should use relevant signboards to warn of possible accidents.
The following are extremely important both for analysis as well as timely action so as to keep the machines running with optimum productivity (microprocessor-based controls):
Stoppages due to mechanical reasons;
Idle stops in terms of breakage per hour;
Time taken by weaver to attend a loom;
Alarms for due maintenance / lubrication schedules.
All findings during scheduled maintenance must be documented in a checklist for future reference so as to check effectiveness at any given time. Timely plans and implementation are important after analysis of the findings from a scheduled maintenance.
Types of maintenance
Scheduled maintenance: With the erection and commissioning of a plant, machine manufacturers provide manuals and various checklists which are based on fixed running times or fixed periods. These checklists are to be followed by the maintenance team on a daily, bi-weekly, weekly, fortnightly, monthly, half-yearly and annual basis.
Predictive maintenance: If the preventive maintenance interval is too short, a machine will be overhauled unnecessarily with a consequent loss of production and possible human errors during dismantling of a sophisticated assembly. Predictive maintenance is an important task that is performed by an experienced person on the actual working condition of a machine.
Some of the criteria for predictive maintenance are given below:
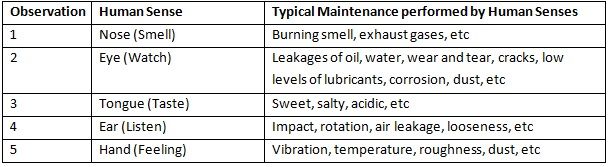
Preventive maintenance: This involves the rechecking of components in similar machines, if there is a breakdown of one machine. If one maintains a strict follow-up in preventive maintenance, the losses due to low production or bad quality can be drastically reduced. It also helps in avoiding maintaining excessive spare part Inventories.
By maintaining equipment and machineries as per schedules, plants can deliver better outputs. One can ensure plant safety, have optimum efficiency, save time in processes, and also make long-term savings in costs. Effective maintenance in a plant is possible only by well-trained foremen and mechanics, and the process itself has to be backed by a clear vision of the top management.
About the author:
Pradeep Kulshrestha has over three decades of experience in administering world-class manufacturing plants and project implementation. Currently, he is DGM (Business Development & Services) with the International Institute of Management and Technical Studies.









Comments