Photochromic dyeing is slowly gaining commercial acceptance
Photochromism is defined as the reversible transformation of a chemical species between two forms by the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, where the two forms have different absorption spectra.
Photochromic dyestuffs are substances that demonstrate the phenomenon of reversible colour change induced by ultra-violet (UV) rays. When sunlight or UV light falls on the surface, the colour is revealed and the colour disappears when the light source is removed. The strength of the colour depends on the intensity of the light source.
Photochromism is the characteristic of several organic and inorganic chemicals. A photochromism-based photochemical reaction either occurs by a rearrangement of valence bonds or by a change in the configuration of the atoms in the molecules, which is also called as cis-trans isomerism. The photochromic colours are plastisol-based inks, which are generally off-white when not exposed to UV light.
The active photochromic dye is contained in a micron-size microcapsule dispersed in water to make-up the pigment. The pigment so formed has the consistency of thick cream. When such pigments are mixed with a binder like acrylic base, it can be applied to almost any surface. The intensity for colour change depends on the consistency of the pigment. The more diluted the pigment, lesser is the colour change. So the mixing is generally done on a trial and error basis.
Inko-dyes: Light-sensitive vat dyes
Inko-dyes are vat dyes, but instead of being applied on oxygen-free bath and then locking in fabric by exposure to oxygen, it is developed in light.
The steps are as follows:
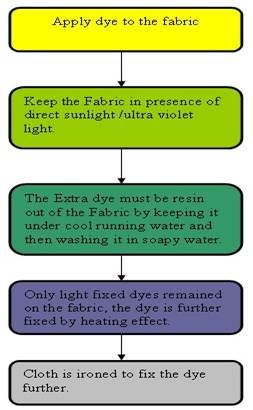
Inko-dyes can also be fixed by heat. These dyes have wide application in various fields. These are used for various garments like T-shirts, security-badges.
Charateristics
Photochromic dyes can be dissolved in various organic solvents like methlyethylketone, toluene, xylene and ethyl acetate.
- It can be mixed with other regular dyes to have effect of colour-to-colour.
- By mixing primary colours, a colour can be matched to show colourless or light colour-to-colour.
- Different photochromic dyestuff have different heat resistance.
Applications of photochromic dyes are limitless.
Some of its applications in textiles are the following:
1. Creating novel products and promotional items like T-shirts
2. Printing company logo or brand name on a fabric or garment to prevent duplication
3. Party wear apparel
4. Thermometers and temperature indicators
5. Security printing
6. Block printing, stencilling and screen printing on fabric
7. The photochromic dyed textile provides various opportunities and flexibilities for dyeing and creating designs:
-
Fabric dyeing and then garment designing
-
Fabric printing and then garment designing
-
Screen printing after garment designing
-
Using photochromic as main body and trim patches.
8. Fashion items, UV indicator, UV-protection, sportswear, outdoor workwear and kidswear.
Its disadvantages include higher costs over general dyes and non-resistance to laundry.
The up-coming concept of photochromic dyeing is slowly gaining commercial acceptance. It is expected that it will create a new trend in the dye and the textile industries.
Source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photochromism
http://www.forscher.com.br/ingles/foto_cromicos_ingles.htm
http://www.thesmarttime.com/articles/photochromatism.htm
http://www.pburch.net/dyeing/howtodyewithlight.shtml








Comments