Fibre2Fashion enumerates the various policy reforms undertaken by the Indian Government to boost the textile-garment sector
India, the second largest exporter of textiles and apparels in the world, has a big manufacturing base and high raw material support. The textile industry is one of the major contributors to the country's economy. It holds a 7 per cent share of the total industrial output, 2 per cent of the total gross domestic product (GDP) and 15 per cent of the total income from exports. About 45 million people are employed in this industry.
The ministry of textiles and related government organisations have taken multiple initiatives last year to boost Indian trade, preferably exports.
Tariff Reforms
Here is a list of product-specific reforms undertaken by the government:
July 2018
The government has doubled import duty for 50 textile products like jackets, suits and carpets. The duty was raised to 20 per cent from 10 per cent to promote domestic manufacturing industry.The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) also increased the ad-valorem rate of duty for certain items. Hence, the import of the woven fabrics, dresses, trousers, suits, baby garments and a variety of knitted fabric became expensive. But still India allowed duty free access to least developed countries like Bangladesh.
The textiles ministry imposed anti-dumping duty of up to $528 per tonne on import of polyester yarn that is majorly used in automobile and other industries. The duty imposed is in the range of $174-528 per tonne. It will be effective for five years. High tenacity polyester yarn (industrial yarn) is used for manufacture of tyre cord fabric, seat belt webbing, conveyor belt fabric, ropes, coated fabric and automotive hose.
August 2018
The government again doubled the import duty on textile products to further incentivise the domestic textile and clothing industry. It included 328 tariff lines of textile products and tariff increased from 10 to 20 per cent. This move made imported garments, fabrics, carpets and specialised fabrics costlier. Higher duty was imposed on shirts, trousers, coats, blazers, kids garments and lingerie.
October 2018
According to the Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR), nylon filament yarn (multi-filament) was being exported to India from the European Union (EU) and Vietnam below normal values. Hence, the government imposed anti-dumping duty on import of nylon filament yarn, mainly used for curtains, embroidery threads and fishnets, from Vietnam and the EU, ranging between $128.06 and $719.44 per tonne. The duty is effective for five years starting October 6, 2018.
The government imposed definitive anti-dumping duty on a flax yarn (100 per cent linen yarn) used in fabric industry from China. It ranged from $1.30 per kg to $4.83 per kg depending on the producer and exporter from China.
December 2018
-
The duty drawback rates across all varieties of textile and apparel was raised to 70 per cent to promote textile and clothing exports.
Major cotton products with high increase in duty drawback rates
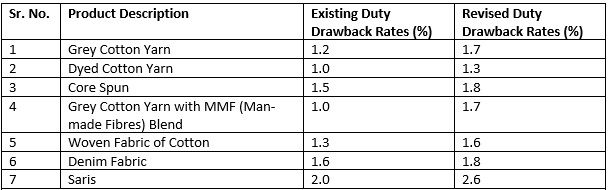
Source: Ministry of Commerce, India
-
According to KV Srinivasan, chairman of the Cotton Textiles Export Promotion Council (TEXPROCIL), the revised duty drawback rates would increase the exports of cotton textiles and other products in the value chain. The significant increase in the duty drawback rates for cotton made-ups would encourage the export of value-added products like home textiles. Also, the removal of drawback cap in case of export products with less than 2 per cent of the duty drawback rates would benefit cotton textiles exporters. This would help exporters face competition overseas. An additional product, nylon filament yarn (dyed), was also added under the drawback scheme.
Non-Tariff reforms
Here is a list of subsidy rules, schemes and initiatives implemented by the government and associated trade bodies:
July 2018
-
In the 28th national handloom award function, minister of textiles Smriti Irani announced that 90 per cent subsidy would be provided to handloom weavers for technological upgradation. She also discussed the implementation and benefits of the Mudra scheme.
August 2018
India and Singapore signed the second protocol amending the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) to boost bilateral trade. The provisions of the second protocol came into effect the following month. Both sides agreed to expand the coverage of tariff concessions, rationalise product specific rules, liberalise rules of origin and include provisions on certificate of origin and cooperation on its verification.
September 2018
-
India and Morocco signed an agreement to facilitate the transfer of Indian technologies and products to the North African nation through micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs). The major Indian exports to Morocco include textile products like cotton yarn and synthetic fibre. Morocco could become a gateway for India's exports to Europe, West Africa and the United States as it has a plethora of trade treaties with several countries and entities.
December 2018
-
The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and the Shanxi Provincial Committee of the China Council for the Promotion of International Trade signed a cooperation framework agreement to strengthen bilateral trade. The trade between the Shanxi province and India primarily focused on textiles and a few other sectors. Shanxi province's imports from India includes cotton yarn.
January 2019
-
India included merchant exporters under the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) for pre- and post-shipment rupee export credit by allowing them interest equalisation rate of 3 per cent on such credit for export of products covered under 416 tariff lines identified under the scheme. These products are largely in the MSME and labour-intensive sectors, including textiles and apparel.
-
The government announced a special package for garments and made-ups sectors to help reforms in labour laws, additional incentives under the Amended Technology Upgradation Funds Scheme (ATUFS), enhanced duty drawback coverage and relaxation of Section 80JJAA of Income Tax Act. The rates of the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) were also increased from 2 per cent to 4 per cent for apparel and 5 per cent to 7 per cent for made ups along with handloom and handicrafts with effect from November 1, 2017.
March 2019
-
A scheme for rebate of all state and central embedded levies for apparel and made-up textile segments were approved to make shipments zero-rated and boost the country's competitiveness in export markets. As the MEIS scheme would not be available beyond December 31, the Remission of State Levies (RoSL) was revised upwards for garments and made-ups to offset the disadvantage. The shipments from Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Vietnam have been enjoying zero duty access to the EU, which is the biggest export market for India's apparel sector. At present, RoSL has been provided to textiles exporters to offset indirect taxes levied by states, such as stamp duty, petroleum tax, electricity duty and mandi tax. The decision that extended rebate up to March 31, 2020, would greatly benefit apparel and made-ups players.
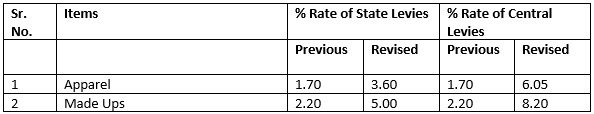
May 2019
-
The government announced plans to launch a Social and Labour Convergence Programme (SLCP). It would be compatible with existing audit systems and codes of conduct. The same dataset can be used by a wide range of stakeholders.
June 2019
The Indian textile minister announced a package of ₹50 crore for the knitwear sector. Under the SAMARTH scheme, training would be given to one lakh workers. All pending cases of TUFS would be cleared expeditiously from the office of the textile commissioner.
Khadi Promotion
Remarkable initiatives were initiated by the government to make khadi a global brand:
-
Khadi Mark was notified to ensure its genuineness.
-
The Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) was given the status of deemed export promotion council to promote khadi.
-
Tie-ups were arranged with premier government organisations and promotion councils, including the Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO), the World Trade Centre (WTC), the Indian Trade Promotion Organisation (ITPO), the National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) and the Trade Promotion Council of India.
-
KVIC promoted khadi on the 72nd Independence Day celebrations in 10 Indian consulates abroad and exhibited khadi products under 'Global Khadi' name in 57 Indian embassies.
-
A separate HS code for 22 khadi items was requested from the ministry of commerce.
-
Ten KVI institutions from Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka, Gujarat and Kerala participated in an international exhibition in St Petersburg, Russia, organised by the ITPO in March 2019.
-
KVIC introduced fashion designers of national and international repute for designing that would help khadi products turn more competitive and appealing in the domestic and overseas market.
-
Financial support under international cooperation scheme for technology infusion, up-gradation of MSMEs and promotion through exhibitions and trade fairs.
-
Assistance provided under the Market Promotion and Development Assistance (MPDA) scheme to the eligible KVI institutions for participation in international exhibitions and trade fairs.
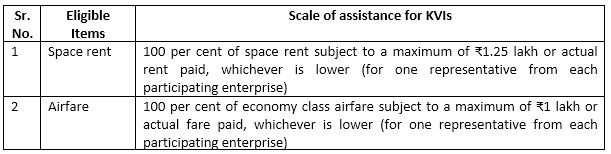
Reforms in Industry Infrastrcuture, Logistics and Other Services
From July 2018 to June 2019, the following reforms were initiated:
1. Cabotage rules were made easier and domestic freight was opened to foreign ocean carriers.
2. CBIC revamped its policy for inland container depots.
3. Bangladesh ports were approved for Indian shipments to the North-east.
4. A national trade portal was launched to cut logistics costs.
5. Import-export clearance time was cut by 300 hours.
6. The Indian cabinet cleared the amendment to currency swap framework for SAARC countries.
7. The bilateral currency swap arrangement between India and Japan was approved by the cabinet.
8. India and Mexico inaugurated a business chamber to encourage more trade and investment.
9. India and Kyrgyzstan came out with a five-year roadmap to boost bilateral trade.
Indian Textile-Apparel Trade Forecast
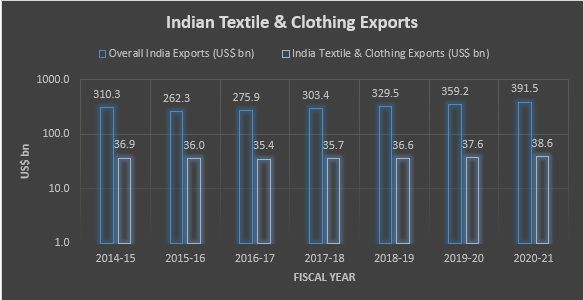
Source: Ministry of Textile, India
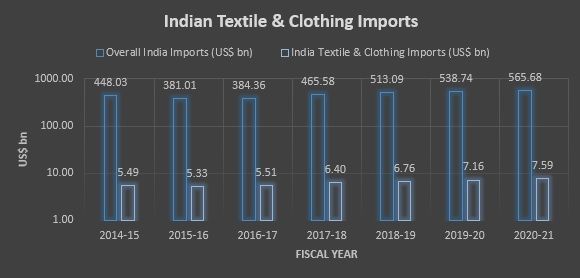
Source: Ministry of Textile, India
Work under way
July 2018
-
Expansion of India-ASEAN free trade agreement
-
India to replace export subsidy schemes banned by the Word Trade Oraganisation.
-
India to offer free trade pact with Mauritius.
-
Container shipping lines and port operators have urged the government to upgrade the India-Bangladesh coastal shipping agreement to get permission for transhipment of Bangladesh cargo from Indian ports.
-
India to impose anti-dumping duty of up to 719 per tonne for five years on import of nylon filament yarn from the European Union and Vietnam.
-
The ministry of commerce and industry has proposed an industrial policy with provision for the manufacturing in the textile sector to boost growth.
-
Minister Suresh Prabhu proposed a target to double bilateral trade with Iran in next five years.
-
India is expected to sign a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with Bangladesh.
-
EU was expected to rework an FTA with India in the post-Brexit scenario.
-
India and Mauritius will probably sign a free trade pact in January.
-
India has tried to push for a free trade pact with the United Kingdom as appoximately 800 Indian companies use the country to enter the EU. Being one of the biggest forex earners in the country, India's textile-garment sector was extremely keen in such a pact.
-
India and South Korea to work on improved utilisation of the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to expand negotiations on bilateral trade and investment.
-
India and Peru held the fourth round of FTA talks in Lima in March. This FTA would be much beneficial for India as India was the major cotton yarn and fabrics exports to Peru.
-
India and Iran held the fifth round of negotiation for a bilateral preferential trade agreement (PTA). With the help of this. strategic products, including textiles and readymade garments, which attract very high duties in Iran, could become more competitive.
-
India proposed a WTO-compliment schemes to boost Make in India.
-
The India-Nepal Treaty of Trade and Transit would be amended soon to include waterways as a mode of cargo transport to enhance connectivity between the two countries.
August 2018
September 2018
November 2018
March 2019
May 2019
June 2019








Comments