Indonesia is among the top 10 textile producing nations in the world and a leading textiles and apparel producer in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region. A Market Intelligence (MI) report from Fibre2Fashion.
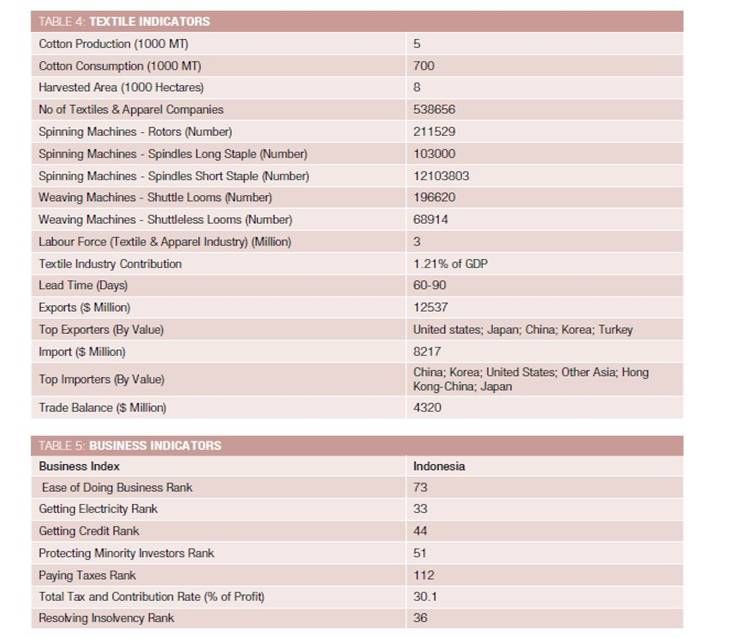
Being one of the largest textiles and apparel producers in the region, the country has a long tradition of producing and exporting ready-made garment and home fashion textiles. The country is the 12th largest textiles and apparel exporter with major export destinations, including the United States, European Union and Middle-East. It also continues to be a leading textiles and apparel producer in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region. The Indonesian textiles industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.09 percent in terms of revenue during the forecast period of 2018-2023. Despite global decline in textiles demand, the overall textile exports of the country rose by 5 percent on a year-on-year basis in 2017, according to the Indonesian Textile Association (API). The burgeoning business can be attributed to growing textile exports to its three primary destinations.
Open for business with the world
Even though most of Indonesia's several thousand textile businesses sell their goods in the domestic market only, the lion's share of Indonesian-made clothes is shipped abroad, with many of the larger companies producing apparel for global brands. China is the main source of textile products coming into Indonesia, followed by South Korea. One of the sector's key strengths is the rare presence of both an upstream and downstream industry, both of which are well developed. Indonesian textiles companies have been quick to align themselves with international industry standards by making the necessary investments to achieve certifications such as ISO 9001 as well as gain recognition for sustainable and environment-friendly production.
Source: TexPro
SWOT Analysis of Indonesia
Strengths:
1. Vertically integrated garment and textiles industry.
2. Large domestic market.
3. Good government support to industry in financial and regulatory terms.
4. Low cost of production.
5. Good labour skills recognised by importers from developed nations.
Weaknesses:
1. Absolute dependence on cotton imports, partially offsetting cost advantage.
2. Obsolete technology in production processes leading to lower productivity.
3. Low compliance to sustainability and quality standards requirement set by customers from developed nations.
4. Low profitability due to lack of direct contracting with international brands.
5. Lack of supportive infrastructure.
Opportunities:
1. Free trade agreements with high income economies to expand the market size.
2. Imposition of safeguard quota on several textiles and clothing products from China by EU and US.
3. Opportunities for global and regional exports.
4. Increasing consumption in the domestic market.
Threats:
1. International environmental management standard certifications to highlight criteria to choose supplier from developing regions.
2. Face significantly growing competition from other Asian countries such as Vietnam, Bangladesh and China.
3. Unfair competitive business practices and violation of international laws.
4. Non-participation for trade agreements providing competitive edge to competitors in major markets of EU and US.






Comments