Yamini Jhanji Dhir reviews digital printing, its advantages and its application in designing fashion accessories
What is Digital Printing?
Digital printing is the latest printing technique that involves the creation of prints with the aid of designs conceptualised using computer software. The technique is gaining popularity over other troublesome and time consuming printing techniques like roller, screen and transfer printing owing to cost effectiveness. Designs too can be repeated. The technique finds application in designing a range of apparels, accessories and home textiles.
Accessories engineered and designed from knitted fabrics are the latest rage among consumers who simultaneously seek comfort and aesthetic appeal in the same product. Knitted accessories are not only comfortable owing to good moisture, air and heat transmission properties, but can also be decoratively embellished to offer an appealing look. Several surface embellishment techniques, such as hand painting, crocheting, applique work, addition of trims and notions and digital printing, can be applied to beautify knitted fabrics and accessories.
Digital printing is the process of creating prints using designs from a computer as a reference as opposed to analogue printing, which requires screen printing. It was introduced in 1950 for paper printing but the technique was later deployed for textiles as well. It emerged as a prototyping tool and a vehicle for printing small batches of fabric for niche market products, namely apparel, accessories and home textiles. It shortens the lead time from design to production, speeds up sample production and reduces production lot size and inventory costs.
Digital Printing Process
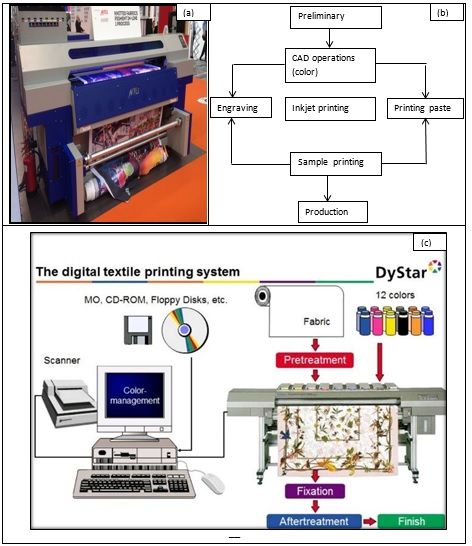
Design selection and conceptualisation is the preliminary and most crucial process before digital printing on textile substrates. Fabric is printed by digital printers with the design prepared on computer using inkjet-based method of printing colourants onto fabric (Figure 1 (a-c). Hand drawn sketch, computer-aided design (CAD) sketch of designs are utilised and edited using various tools available in software like CorelDraw and Adobe Photoshop. The files obtained are utilised on digital printing machines to print the design on to fabrics. The printing process involves feeding the fabric through the printer using feed roller followed by application of ink on the fabric’s surface in the form of thousands of tiny droplets. The fabric is then passed through steam/heat chamber to cure the ink. The steamed fabric is subsequently washed and dried. The advancements introduced in digital printing machines involve the installation of special transport systems that enable printing on knitted and stretch fabrics. Figure1 (a) shows the model of digital printing machine that is generally employed for printing on textile substrates.
Fig. 1- (a) Digital printing machine (b) Design production process (c) Digital textile printing system
Fabric Preparation for Digital Printing
Smudge free printing and superior quality that exactly replicate the motifs or designs are the prerequisites while digitally printing on textiles. Accordingly, the fabric needs to be prepared—coated with chemicals—before the process starts. The fixation of ink received by the fabric during the printing process is assured by the curing process that follows printing. Curing is accomplished by passing the fabric through steam/heat chamber, followed by washing and drying. Pre-treatment technology is used to obtain vivid colours, darker blacks, sharper definition and excellent wash durability, without any adverse effects on fabric hand. The technology ensures excellent adhesion of ink to the textile medium. Apart from the padding method of pre-treatment, spray method using compact Swift jet model is also commercially used to work in-line or separately from the ink-jet printer, thus eliminating the need of pre-treatment by padding. The spray drop size can be varied to enable variable pick-up based on the substrate. The spray application ensures precise control for woven, knitted and piled fabrics that may be subjected to crush during the padding process.
Different knit structures like single jersey, rib and interlock structures composed of a range of fibres and their blends—namely cotton, viscose and polyester—are being printed digitally. Fibres with high moisture content ensure increased dye uptake and thus brighter colours and brilliant shades of the final processed fabric.
Although digital printing is done on a range of woven and knit fabrics, trials on rib knit fabrics have been successful as the rib structure is tight, enabling sound ink penetration and the images are not disrupted by stretching or curling like in plain knits. Further, owing to soft jersey construction on face and back side, rib knits are comfortable to wear.
Pros and Cons of Digital Printing
Digital printing enables manufacturers to streamline the entire design, sampling and production process. Reduction of downtime is one of the biggest benefits. Digital printers do not require lengthy set-up or clean-up time between patterns and can still produce the finest print qualities. Additionally, elimination of screen cost in sampling and short production runs is another added advantage. Mass customisation is possible as the system provides flexibility to designers to make pattern and colour changes instantly and print a sample before engraving screens for the final run. Digital production machines facilitate the printer to produce as little as one repeat of several patterns using multiple colour ways in a fraction of seconds.
The motifs or selected designs can be printed all over as repeat patterns, borders or on hemline as per the designer’s design ideas posing no difficulty of printing even at the edges. The bonding of the dye to the transparent fibres of the synthetic fabric ensures extraordinary brilliance of shades and hues of colours. Digital printing saves time and cost for sampling. Continuous tones can be achieved that are equivalent to photographs, unlike half-screen and screen printing that necessitates the preparation of screen and provides limited colour options.
Digital printing improves printing efficiency and offers an array of vivid innovative prints, colour palettes and speed. The speed and cost effectiveness of single-pass printers are comparable to rotary screen printing. Variable drop sizes in print head, fabric handling, nozzle failure and fabric wrinkle detection system, reduced environmental impact and higher uptime of the printer because of no screen changes are some of the features that modern digital printing systems offer.
However, the technique has some disadvantages as well. It is time saving for sampling only. Moreover, sampling and production cost is high with higher cost and lead time for bigger production runs. Another disadvantage is slow speed of the process.
Accessories Designing with Digital Printing
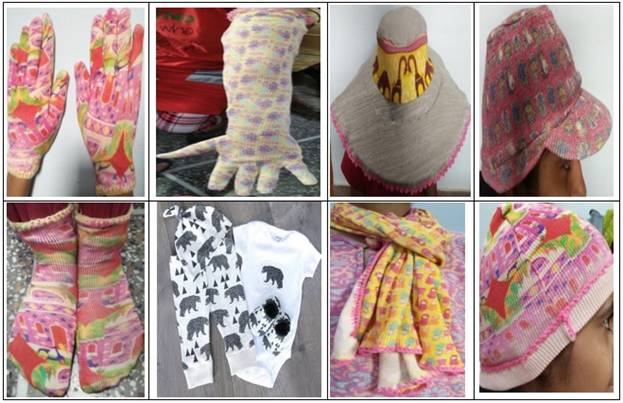
Digital printing is used as a surface embellishment technique for designing a range of fashion accessories like scarves, socks, stockings, head accessories, gloves and footwear. Inspiration of motifs chosen for digital printing can be taken from flora and fauna, human figures, mythological characters, architecture and geometrical patterns. The colour combination and design themes can be vivid from subtle, pastel shades to vibrant, exuberant and lively. Figure 2 shows some of the motifs chosen for digital printing. The motifs can be strategically chosen to beautifully design and embellish the accessories. The selection of motifs is followed by creation of mood board and storyboard as shown in Figure 3. Figure 4 shows various accessories designed using digital printing.
Fig. 2 – Motifs for digital printing on accessories

Fig. 3 (a) – Moodboard& (b) story board creation for designing accessories
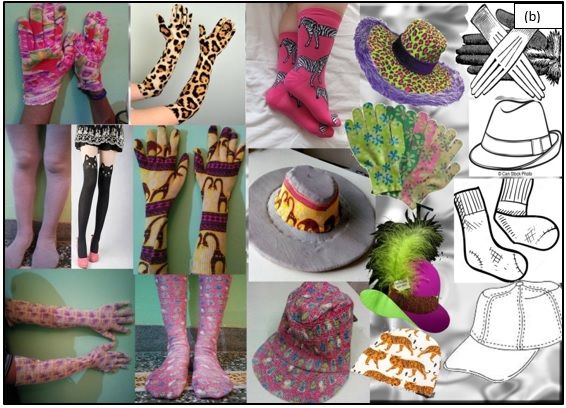


Fig.4 – Knitted accessories designed using digital printing technique

References
1. Spencer P &Schwartzwald D, Automatic Print Quality Measurement Using a Scanner, In: 12thInternational Conference on Digital Printing Technologies, 1996, 1-3.
2. Wang PL, Print Image Quality Evaluation System, In: 10th International Congress on Advances in Non-Impact Printing Technologies, 1994, 5-10.
3. Yoshimura K., Kishimoto M &Suemune T, Inkjet Printing Technology, Techn Review, 64 (1998) 1-5.
4. Parsons, Taking advantages of The Design Potential of Digital Printing Technology for Apparel, J Apparel Tech Manag, 4(3), 2005, 1-6.
5. Mejtoft T, Strategies for Successful Digital Printing, J Media Bus Studies, 3 (1), 2006, 1-5.
6. Hada S & Shah M, Digital Printing of 100% Viscose Knit Fabric, Fibre2Fashion.com.









Comments