Nonwovens is one of the fastest-growing sectors of the textile industry and constitutes roughly one-third of the fibre industry. Their popularity today is partly due to their superior absorption, softness, good moisture retention capability, but mostly because of their relevance in the current pandemic situation. Since the onset of COVID-19, nonwovens have been extensively utilised in the healthcare and foodservice industry. The popularity has led to an increase in its market value to an estimated $43 billion in 2020, which is only expected to further register a CAGR of over six per cent between 2021-2026.
This article covers the topic of nonwoven fabrics and various processes involved in turning nonwoven fibres into nonwoven wipes. It also discusses the biodegradable and non-biodegradable aspects of the material along with the IP analysis of the nonwoven industry at large.
Nonwoven Wipes
Wipes are one of the common products that are required daily for various purposes. A wipe is a small piece of cloth used for cleaning or disinfecting. Nonwoven wipes have recently gained popularity because of their excellent absorption and softness. They tend to have sound absorption, smooth and soft texture, and good moisture retention, and are available as dry wipes and wet wipes.
While nonwoven dry wipes are just like a regular cloth in their appearance, in the case of wet wipes, the nonwoven fabric is impregnated with a dual solution – they obviate the need to use separate wet and dry combinations while cleaning, thus gaining popularity over dry wipes. Moreover, they have a smooth and soft texture, good absorbance characteristics, and good moisture retention properties. Thus, allowing the user to perform tasks with better efficiency in substantially lesser time.
Demand for Nonwoven Wipes
The demand for wipes has been growing due to several factors, such as increase in disposable income of consumers, changing lifestyles, product innovation and the growing need to adapt to a sustainable option. On top of it, the recent challenging times of the post-pandemic world have pushed their utilisation in the foodservice and healthcare industries due to the heightened health and hygiene concerns. Further, product innovation is also a factor that boosts the demand.
Other than these external factors, the demand is also increasing due to the inherent qualities of nonwoven materials. For example, they are cost-effective, easier to use, more versatile, safer, and have better disposability when compared to other textiles. The fibres are usually blended or mixed, which can be natural/natural, synthetic/synthetic, or natural/synthetic. It improves performance-related properties of nonwovens, such as strength and other properties.
Patent Filing Trend
One of the ways to understand the technology direction and investments is to analyse the patent filings, their applicants, jurisdictions, etc. Here, different charts have been shared to represent the top companies, filing trends of the technology, and jurisdictions of most patent filings.
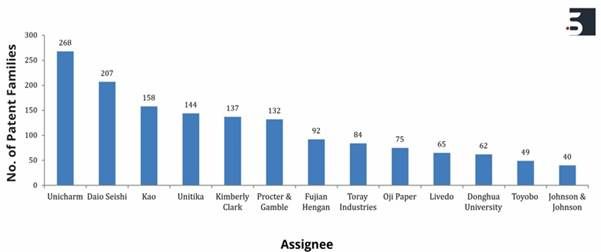
Chart 1: The top organisations that make up the top assignee list. It shows that the top assignee has made significant strides towards the nonwoven wipes industry.
The filing trend of the top assignees is given above wherein, Unicharm has the most patent filings followed by Daio Seishi, Kao and Unitika. Further, Kimberly Clark, P&G, Fujjain Hengan, Toray Industry, Oji paper take the spot. Additionally, Livedo, Dongua University, Toyobo and J&J are also among the top assignees for filing patents in the field of nonwoven wipes.
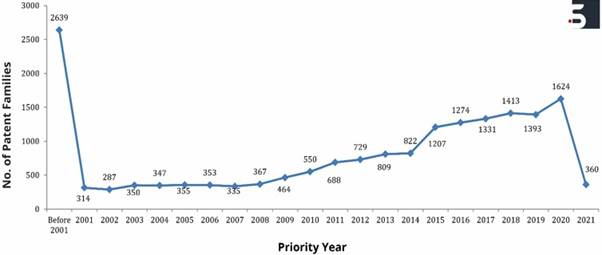
Chart 2: The filing trends in nonwoven wipes market from 2001 to 2021
Note: The data for 2019, 2020 & 2021 might not be complete, since it takes 18 months in general for a patent application to be published in the public domain.
As Chart 2 suggests, the filing trend has been increasing steadily and at a higher pace since 2009. One reason for the steady growth of patent filings can be dedicated to the increase in the awareness and demand for sustainability.
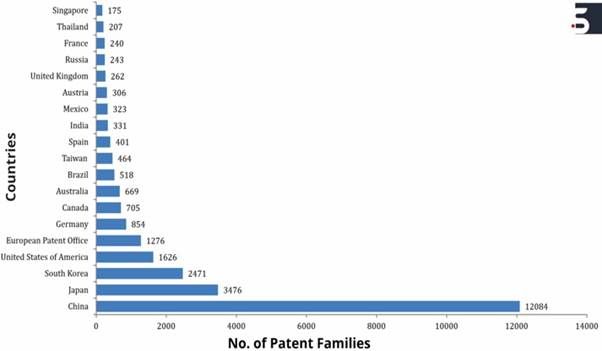
Chart 3: The distribution of patents by countries. The chart identifies the counties by the number of patent filings, thus, representing the origin of the research.
Chart 3 demonstrates that China, Japan and Korea have the highest filings, followed by the US, EP and Germany. Further, Canada, Australia, Brazil, Taiwan, Spain take the spots. India stands at 12th position in patent filings which is then followed by Mexico, Austria, United Kingdom, Russia, France, Thailand, and Singapore.
Nonwoven Wipes and Fabrics
A nonwoven fabric is a material wherein the fibres are bonded together by chemical, mechanical, heat, or solvent treatment instead of getting woven or knitted. These fabrics are highly versatile in fibre structure, composition, and performance. Moreover, its manufacturing industry is quite profitable and sophisticated. Due to its high utility, nonwoven fabrics carry an excellent opportunity of penetrating a range of markets including medical, apparel, automotive, filtration, construction, geotextiles, and protective equipment.
Nonwoven Fibres
In general, fibres refer to filaments or threads woven, knitted, matted, or bound to make fabrics for different purposes. In perspective, a piece of fabric is made of yarn, and the yarn is made from fibres. Fibres are then broadly divided into natural, synthetic or man-made. The following chart shows different types of fibres used in the nonwoven domain.
Nonwoven and fashion
Nonwovens are an ideal material for the fashion industry. For many decades they have been used in hidden functions, such as interlinings and components of shoes and bags. The elegance, style and function of clothes can depend on the presence and performance of interlinings. Further, the success of nonwovens is due to their versatility and the ability to engineer many different properties into them, such as shape-retention, adaptation to the characteristics of the outer fabric and lightness in weight. Nonwovens have made an astonishing progress in fashion apparel. Recently, many patterns of fashion garment are developed by using the newly developed nonwoven fabrics. Unlike woven and knit fabrics, nonwovens do not tangle; therefore, this makes it easy to incorporate shaped hemlines into the garment design. Seams within the garment also do not require finishing. Nonwoven fabrics are easy to cut and offer a wider range of design than woven fabrics.
Conclusion
The wide availability of bio-based fibres and binders and the related technology allow the production of fully biological materials. These could completely replace some of the existing conventional nonwovens used as disposable articles, bringing hope to the environmental issues. In the past, sustainability advancements in nonwoven products were made by the improvement of intrinsic hydrogen bonding capability of natural fibres, the use of ionic liquids, and the functionalisation of its surfaces. Furthermore, the engineering works on the machinery allowed the introduction of natural fibres in the production. Additionally, the developments in materials science, polymer chemistry, and fermentation technology improved the properties of natural and cellulosic man-made fibres and renewable polymer binders produced via microbial. As a result, many natural polymers can be tuned according to the desired properties to input in the final product, such as wood and non-wood fibres, starch and cellulose derivatives, and chitin and chitosan.
Hence, many challenges and concerns regarding renewable polymers have already been addressed by researchers. And since the demand is already increasing, it has become imperative that research and industry work closely to introduce bio-based solutions in their process.








Comments