Plastic waste from PET bottles is the major cause for generation of huge piles of garbage around the world. PET being a petrochemically synthesised polymeric compound is a serious threat to the environment as it is non-biodegradable and causes land, water, and air pollution. Chemically, PET is polyethylene terephthalate, a form of polyester extruded or moulded into plastic bottles and containers for packaging food, beverages, and consumer products. PET is widely used and is the most preferred packaging material owing to its transparent form, lightweight, high strength, and low-cost aspects. The post consumed PET waste is usually discarded and thrown as garbage.
Reduction, Reuse and Recycle are the three possible ways to minimise the menace of such PET bottle garbage. However, due to the various consumer-friendly usage benefits and cost-effectiveness, the ‘Reduction’ in consumption seems least likely, rather the production of PET is continuously increasing due to its growing demand. Though the ‘Reuse’ of PET material is often done in developing economies, but the extent of such reuse is limited. Therefore, the only way to control this threat is to ‘Recycle’ waste PET bottles.
The recycling of PET bottles enables the conservation of natural sources such as fossil fuels, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, lowers the carbon footprint, and creates new business opportunities. Therefore, recycling of PET bottles is considered the best option to economically reduce PET waste. The major advantages of recycling PET bottle garbage waste are:
• Reduces landfill area
• Avoids water pollution
• Minimises soil contamination
• Lowers petroleum consumption
• Helps create wealth from waste
• Improves sustainability
The PET waste is converted into r-PET (Recycled PET) for making garments, and both apparel brands as well as fashion-savvy consumers are found to be keen and enthusiastic to try such garments made from waste PET bottles. Moreover, as the petroleum prices increase, r-PET becomes financially feasible in place of manufacturing virgin PET. The current trend indicates that the recycling of PET waste will reach 25 million tons by 2025.
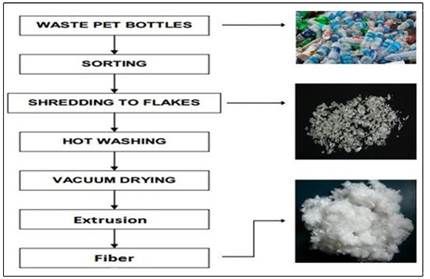
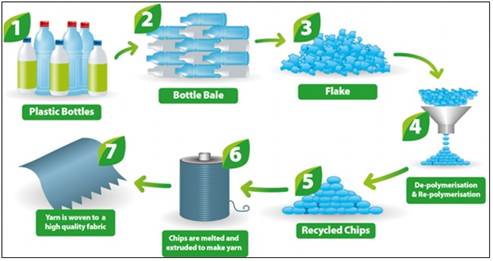
Producing r-PET: The steps involved in this process are as follows:
1. PET bottles are sterilised, dried, and crushed into small chips
2. Chips are heated and passed through a spinneret to form strings of yarn
3. Yarn is then passed through a crimping machine to create a fluffy texture
4. Yarn is then baled, dyed and knitted into polyester fabric.
Advantages of r-PET over virgin PET
• r-PET prevents plastics from being incinerated, landfilled or ending up as marine litter.
• It requires significantly less energy saving almost 50 per cent CO2 emissions.
• It reduces the demand for crude oil and natural gas and controls emissions from incinerators.
• It has different applications, such as textiles, insulation, chairs and benches.
• It enables brands to deliver on their sustainability goals.
Some limitations of r-PET
Weakening of tensile strength
Yellowing and discolouration
Reducing shade brightness
Increasing micro-fibre formation and pilling

Remedial measures
1. Use adequate surfactant. This helps in overcoming interfacial tension between water and dirt/oil/soil and enhances cleaning efficiency. Removes contaminants by solubilising, suspending or emulsifying mechanism. The resultant effect improves the base whiteness of r-PET.
2. Increase cleaning temperature. This provides sufficient energy needed to break bonds between soil and dirt. Treatment at 1300C tends to increase base whiteness.
3. Use bleaching agent. Use oxidative bleaches like hydrogen peroxide, sodium chlorite, sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite to get rid of coloured impurities and boost whiteness and the brightness of r-PET.
4. Add fluorescent brightener. Adding a suitable high temperature stable optical whitener in optimum quantity helps overcome the yellowing/dulling effect and improves fibre appearance and brightness of shade.
This way the PET waste can be collected and converted from garbage to garment.









Comments