The drastic change in the demand of textiles in various sectors has led to development in the field of technical textiles. Initially, the textiles were mainly manufactured for decorative and aesthetic purposes. But the advancement in the field of technical textiles led to improvement in the natural and synthetic polymers used for the textiles. So, scientists began to emphasise on the technical and functional aspects of technical textiles, which were manufactured to serve the specific technical requirements used in different textile sectors. The fabrics used as technical textiles are either industrial or high-performance fabric. The reasons for the development of technical textiles are: health and safety, durability, high strength, cost effectiveness, durability, versatility, user friendliness and logistical convenience. The packaging textiles or packtech is a sector of technical textiles which includes packaging materials used for agriculture, industrial, consumer and other products. The packaging textiles includes wrapping and covering of the products. The packaging of the goods has certain purposes like physical protection of the goods and products, information transmission of the product to the customers, marketing, barrier protection and security of the goods.
Purpose of Packaging
The packaging textiles have varied purposes:
Physical protection: The packaging usually provides protection against mechanical shocks, vibration, temperature changes, compression, electrostatic charge etc.
Information transmission: The packaging provides the details of the product regarding the use, transport, recycling and disposal of products. The packaging for products like pharmaceuticals, medical supplies, food products and chemical products are made mandatory by government for information transmission.
Marketing: The packaging could be used by marketers to encourage the potential buyers for purchasing the products. The marketers change the graphic design, shape and physical design of the product packaging to influence the customers.
Convenience: The packaging can be used for enhanced features like handling, recycling, reuse, display, sale, stacking, ease of disposal etc.
Barrier protection: Some products require protection from external environment like moisture, oxygen, air and dust to increase the shelf life of the products. The desiccants or moisture absorbents are sometimes added to the packaging for enhanced protection. The food packages and medical supplies require such type of packaging.
Security: The packaging is also used to reduce the securing risks. The packaging could be made tamper resistant so that the products are safely available to the customer.
Types of Packaging
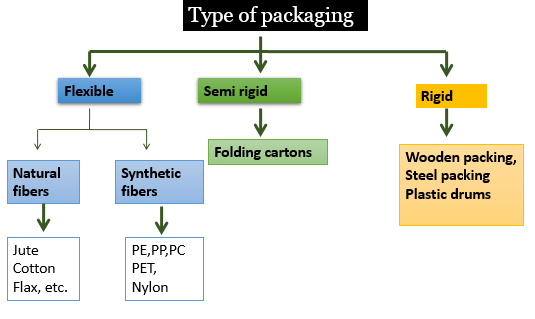
The technical textiles used as packaging textiles or packtech are:
• Polyolefin woven sack
• FIBC
• Leno bag
• Hessian sack/Jute sack
• Soft luggage
• Wrapping fabric
• Tea bags
• Polyethylene foam
• Air bubble sheet
• Polyolefin shrink film
1. Polyolefin woven sack: The polyolefin woven sack is generally made up of polypropylene/high density polyethylene. The sack may be laminated or unlaminated, ultraviolet stabilised or anti slip coated. The polyolefin woven sacks are mostly used for packaging of cement, fertiliser, chemical, food grains, cattle feed, sugar and salt.
Characteristics: High modulus strength, light weighted, minimal seepage, moisture proof, high shelf life, cheap in price.
2. FIBC (Flexible Intermediate Bulk container): The FIBC bags are similar to HDPE/PP bags but are large size bags. The bags are cost effective and made up of woven fabrics. The FIBC bags are ideal for the shipping and storing of dry bulk products. The use of coated or uncoated FIBC vary with weights depending on requirements of safe working load or safety factor.
Types: U-panel bag, four panel bag, circular woven bag, conical bag, baffle or form stable bag.
U-panel bag: The bag is two-piece with two seams which are sewn along two opposite sides overlapping the two rectangle panel pieces to create U shaped panel. This type of FIBC bag is most popular and widely accepted as per the industry standards all around the world. The bag offers one advantage that it provides large lifting capacity of the raw materials.
Four-panel bag: The bag is developed such that the four different pieces of polypropylene are sewn together for the construction of the body of the bag and one upper and bottom panels are stitched to the bag. These bags have one advantage that they are dimensionally stable and are suitable for sacking purpose.
Circular woven bag: The bag is circularly woven into a cylinder or tube-like structure. The circular fabric is used to develop the body of the bag and square base panel is stitched both on top and bottom of the bag. The bag is suitable for use for fine and hydroscopic materials. The bag is also easy to lift and manipulate with forklift.
Circular bag: The bag is specifically designed so that the materials could be completely discharged quickly and easily. The materials for which the bag is required are slightly sticky materials like brown sugar, and premix flour products.
Baffle bag: The bag consists of four baffles sewn to the main fabric at each corner so that bulging of fabrics could be prevented when the raw material is filled into it. The use of baffles allows more effective use of the storage capacity of the bag and also allow the forklift operator easy lifting without additional support. The bag is ideal for light density raw materials and can be more economical as it allows for larger capacity.
3. Leno bag: The leno bags are the woven bags made up of virgin polypropylene and high-density polyethylene. The bags are made up of leno weave and have good mechanical strength with low weight. Such bags are commonly used for packaging of agriculture and consumer products.
Characteristics: Durability, multipurpose bags, cold storage, washable and reusable, less weight, easy handling and storage, economical and cost effective, aeration to the materials for long shelf life.
4. Hessian sack/Jute sack: The bag is also known as burlap which is a finer quality jute fabric. The fabric structure consists of single warp and single weft interlacement while weaving. The bags are light in weight and cost effective. The jute fabric used in the packaging is usually on high demand as it has open weave structure which allows the passage of air so that the contents are protected. The bags are used to store agro products like rice, wheat etc which offers the advantage of being carbon free. The bags are usually treated with vegetable oils to prevent the harmful effect of the hydrocarbons. The Government of India has also regulated compulsory packaging of the food grains and sugar under the Jute Packaging and Material Act, 1987.
5. Tea bags: The tea bags are the small porous sealed bags generally made up of polypropylene. The tea is filled inside these bags and a string is attached to the bag so that tea pouch could be dipped into the liquid. The bag is to be made up of food grade plastic. But it has a disadvantage that small traces of polypropylene could be transferred to the hot liquid. The filter paper used for tea bags is of around 12-17gsm nonwoven material.
6. Soft luggage: The soft luggage is generally made up of woven fabrics like nylon and polyester. The bags include tote bags, duffle bags, sky bags, upright bags with or without handles, handbags, backpacks, wallets, briefcases etc. The bags used nowadays are made such that they are easy to carry, lightweight and flexible. The special feature bags like ballistic proof bags, abrasion resistant bags or fire-retardant bags are developed from special high quality and high-cost fabrics which make the bags costly. Other materials like canvas and coated fabrics are also used for manufacturing of the bags.
7. Wrapping fabric: The wrapping fabric is made up of materials like high density polypropylene, polypropylene, cotton, canvas etc. These fabrics could be laminated or unlaminated woven fabrics. These fabrics have dense weaves in case of woven fabrics like canvas to prevent the material from being drained by allowing water droplets to roll down the fabrics. These fabrics are used as wrapping materials.
8. Polyethylene foam: The foam sheet is mainly used for industrial purpose as well as for transportation purpose. The foam provides the functions like cushioning effect, shock absorption, thermal insulation, abrasion resistance, chemically inactive, non-toxic, ease of fabrication, wide temperature range and oil resistance.
9. Air bubble sheet: The air bubble sheet is developed from two layers of low-density polyethylene sheets. These sheets provide complete protection against scratching, denting and damage from air. The uses include wrapping of automobile parts like handles, seat cushions, and wrapping of electronic devices like computers.
10. Polyolefin shrink films: The film is made up of low-density polyethylene and is used to pack regular and even irregular shaped products like boxes, cups, food materials, cosmetics, drink packs, stationary products etc. The film is usually sealable so that a close packing is ensured.
Conclusion
The packtech or packaging textiles are used for packaging of materials. These textiles serve various purposes like physical protection, information transmission, marketing, convenience in handling and security of the materials. The wide variety of materials are used for packaging like fabrics, high density polyethylene, high density polypropylene, low density polyethylene etc. The packaging textiles could thus be considered as an inseparable part of technical textiles which have found their use along with other technical textiles like home textiles, industrial textiles, protective textiles etc.
References:
-
http://technotex.gov.in/packtech.html.
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Packaging_and_labeling.
-
http://www.teonline.com/knowledge-centre/study-tech nica l-textiles .html.
-
http://www.ivcie.be/en/page.php?pageId=511.
-
https://www.boundless.com/marketing/textbooks/boundless-marketing-textbook/branding-and-packaging-10 /packaging-75/the-purposes-of-packaging-379-4135/.
-
http://www.ivcie.be/en/page.php?pageId=513.
-
http://www.teonline.com/knowledge-centre/study-technical-textiles.ht ml.
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Technical_textile.








Comments