
Export performance of the global apparel industry: An overview
Table 1 presents export data for the fiscals 2018-2030, revealing significant shifts in the global textile and apparel market. The analysis of apparel export trends from 2018 to 2023, along with the projected values for 2024 and beyond, illustrates a dynamic landscape shaped by global economic conditions and evolving consumer behaviour. The peak in 2022 marks a period of robust industry performance, driven by favourable market conditions and strong demand. However, the subsequent dip in 2023 reflects the challenges facing the industry, including disparities in regional growth rates and shifts in consumer spending patterns.
Looking ahead, there is cautious optimism for future growth, although at a more moderated pace. This outlook is tempered by ongoing economic uncertainties and fluctuating market dynamics, which are expected to continue influencing the global apparel export landscape.
Table 1: Trends in global apparel exports between 2018-2030 (in $ bn)
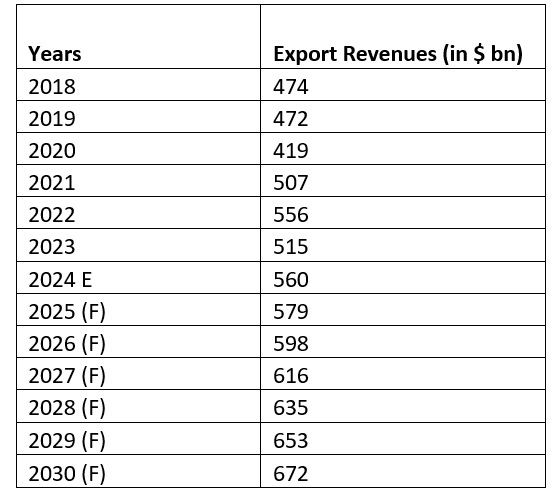
Source: ITC Trade Map, Statista, F2F Analysis
* Please note that values for CY 2024 is estimated and CY 2025-2023 are forecast
Top apparel exporting countries in 2023-24
In 2023, Asian nations like China, Bangladesh, India, Vietnam, and Turkiye dominated apparel exports, leveraging strong manufacturing capabilities and adaptability to market shifts. Outside Asia, the US, Germany, and Italy also stand out for their high-quality production and design. This section provides an overview of the export values from these key countries, examining how they navigate post-pandemic recovery, sustainability concerns, and the rise of e-commerce. The analysis offers insights into the strategies shaping the global textile and apparel sector in a competitive landscape.
Table 2. Global apparel export trends by country
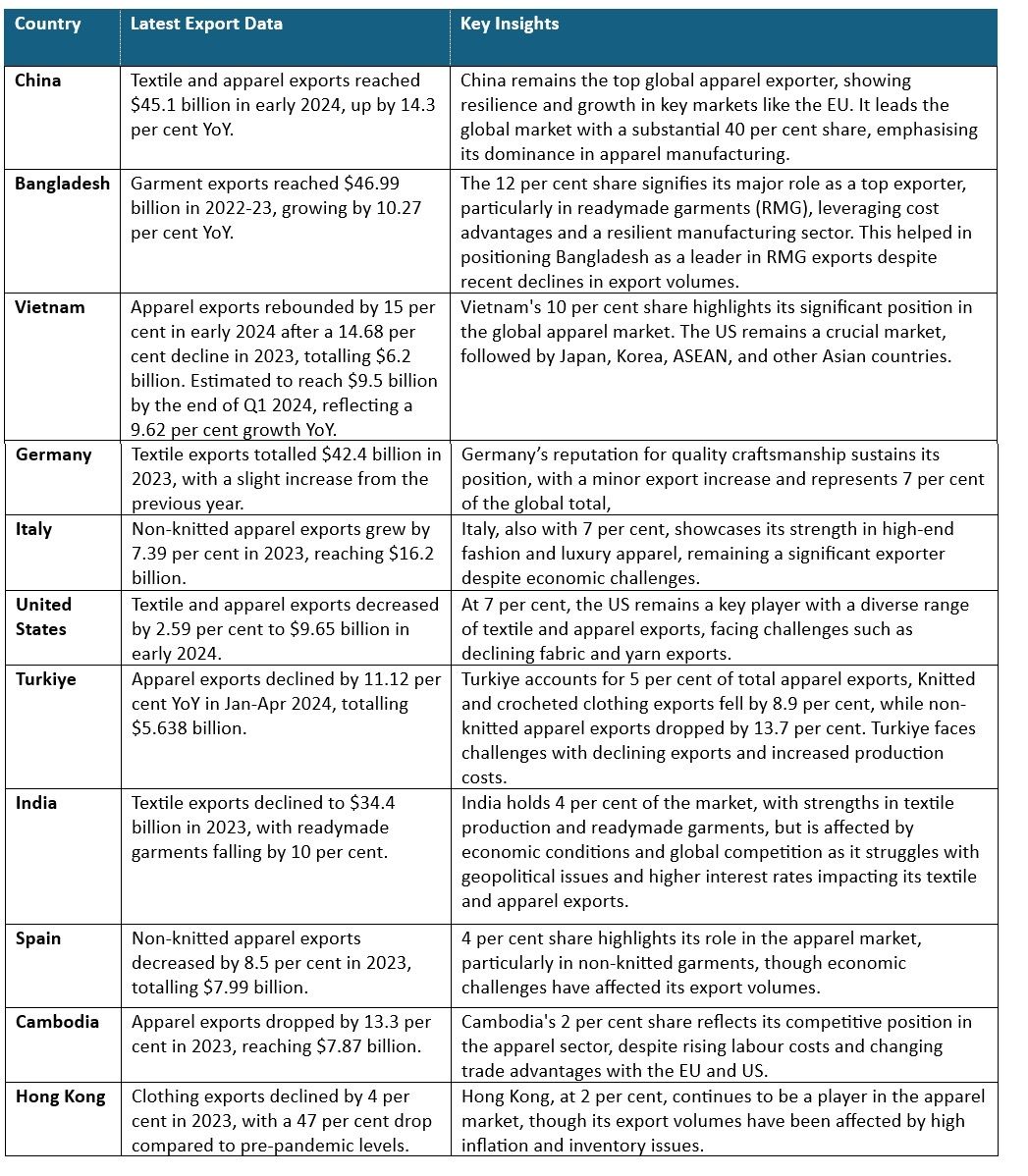
Source: ITC TradeMap, F2F Analysis
Product-wise composition of apparel exports from major exporting countries
The analysis of the product-wise composition of apparel exports from major apparel-exporting countries reveals several critical insights
Table 3: Global apparel specialisations: Leading countries and their key product exports
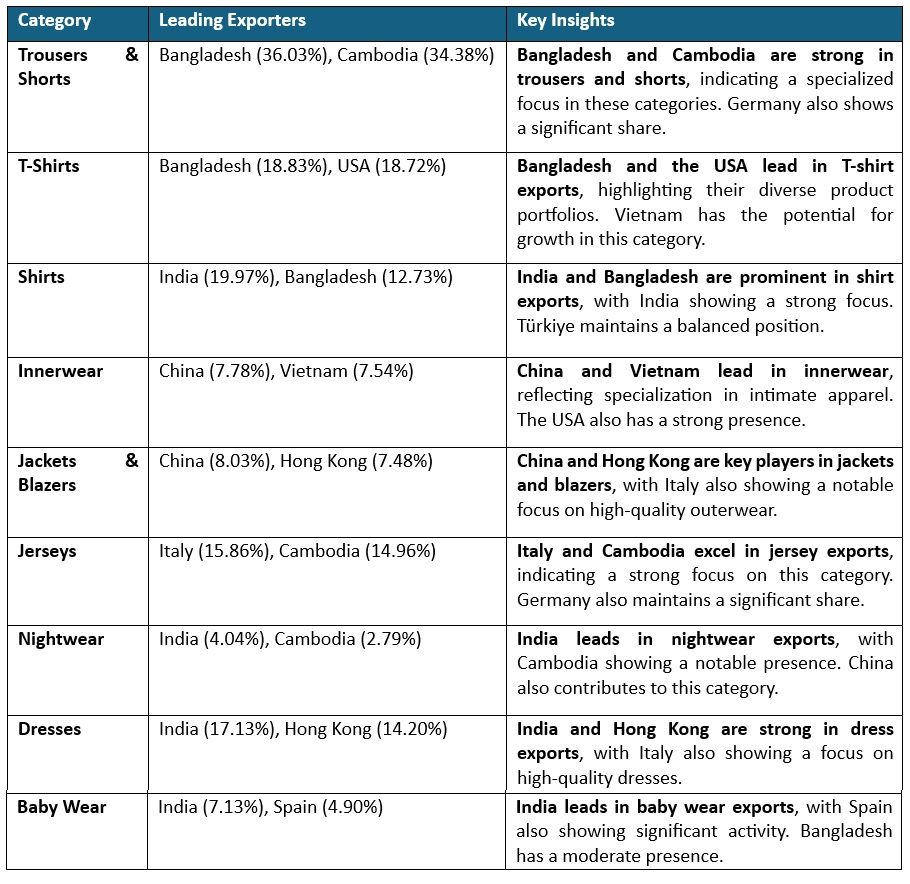
Source: ITC TradeMap, F2F Analysis
Country-specific insights
The global apparel industry is experiencing significant shifts driven by regulatory, economic, and geopolitical factors. Leading exporters like China, Vietnam, Bangladesh, and India face a complex landscape, as sustainability, compliance, and trade regulations shape their market access. China, while dominating the global apparel trade, confronts mounting challenges due to product safety concerns and labour practices, particularly in ESG-conscious markets such as the EU, UK, and US. Simultaneously, Vietnam and Bangladesh, dependent on external inputs, are navigating the risks posed by supply chain disruptions, while Turkiye grapples with economic instability that threatens its apparel sector.
Western countries like Germany, Italy, and the US, though less competitive in mass apparel exports, focus on high-end niche markets but face high production costs. Amid these challenges, exporters are seeking diversification strategies, such as Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and expanding product offerings, to mitigate risks and ensure competitiveness. Compliance with stringent guidelines, especially regarding lab practices and sustainability, remains critical for maintaining access to key global markets. The country-specific insights are outlined below:
China: Despite its dominance in global apparel trade and cost-effectiveness, China faces significant challenges in complying with product safety guidelines. Its large volume of exports to ESG-conscious markets, such as the EU and UK, is impacted by concerns over forced labour practices. The US, a major market for Chinese goods, has been actively working to eliminate products made with forced labour, which could adversely affect China’s trade balance.
Vietnam and Bangladesh: Both the countries rely heavily on intermediate materials like fabrics from other countries. Bangladesh's current crisis poses a risk to its apparel export sector, potentially leading major brands to reduce their sourcing from the country. This situation may create a "Bangladesh +1" scenario, providing an opportunity for other apparel exporters to gain market share.
Turkiye: Turkiye has been grappling with long-term inflation and high interest rates, which have led to the closure of many garment businesses. The country’s ongoing policy-tightening, including a 50 per cent benchmark interest rate, is aimed at controlling inflation and overheating demand, further straining the apparel sector.
India: Indian apparel exporters encounter difficulties with Quality Check Controls (QCC) on raw materials and high import duties, as well as stringent regulations imposed by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT). These internal regulatory challenges significantly impact India's export potential.
Western Countries: Germany, Italy, and the US lag in apparel exports primarily due to higher production costs and a focus on high-end or niche markets rather than mass-produced, low-cost garments. Labour, materials, and regulatory standards are more expensive in these countries compared to major low-cost manufacturing hubs like China or Vietnam. Additionally, these nations often prioritise other industries and their domestic markets, leading to smaller production volumes and less competitive pricing on the global stage.
Economic constraints and market diversification
In particular, the US and Europe, major importers of apparel, are anticipated to face prolonged economic constraints. This situation necessitates that leading apparel exporters, such as China, Bangladesh, Vietnam, and India, diversify their customer bases to mitigate risks. One effective strategy could be the signing of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) that favour apparel exports. Additionally, expanding product offerings can enhance visibility and competitiveness in the global market.
Compliance and sustainability challenges
Sustainability and compliance with stringent regulations are critical concerns for top exporting nations, particularly in Asia. Many of these countries, known for their cost-effective production, sometimes compromise on strict labour laws. Ensuring adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards, along with efficient production practices, is essential for maintaining market access, especially in the EU and US. Exporters should focus on meeting specific regulatory requirements, such as the REACH guidelines and General Product Safety guidelines for the European market, ASTM standards, and CPSIA tracking labels for the US market. Emerging textile exporters like India and Pakistan must prioritise these criteria to avoid costly returns of non-compliant goods.
Fibre2Fashion News Desk (NS)