Key Sustainability Drivers
- Global warming : Greenhouse gas emissions, carbon footprint
- Energy independence : Foreign oil / renewable resources
- Environmentally friendly : Toxicity impact during manufacturing, use
- Biodegradable : Visual pollution, landfill, flushable
- Recycling : Landfill impact
- Sustainable : Overall cradle to cradle environmental impact
- Green : Marketing
Carbon Footprint & Energy Use
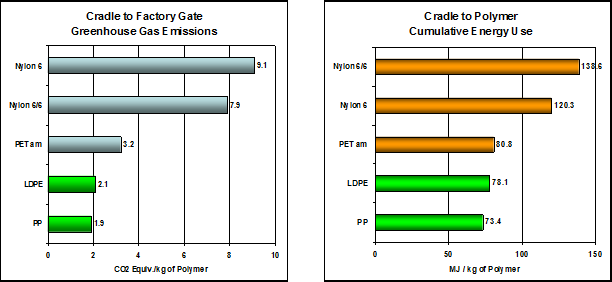
Of the major synthetic fibers, PP is the only one which begins as a co-product of oil refining…with lower greenhouse gas emissions and lower energy use than other fiber resins.
Polypropylene staple fiber has a very high calorific value when incinerated as part of a mixed waste stream, providing a high energy value for the amount of CO2 emitted during incineration. PP fiber is also clean burning, with no toxic emissions.



